Tutorial: Using Impala JDBC and SQL with Apache Kudu

by
Saikrishna Teja Bobba
Posted on
July 21, 2017
Learn how to connect SQL JDBC applications to Apache Kudu using Progress DataDirect in our step-by-step tutorial.
Apache Kudu is a storage manager for the Hadoop ecosystem. Kudu is designed for analytics with a goal of enabling "fast analytics on fast data." Kudu uses a streamlined architecture to store tables with a familiar relational model. Accessing data via SQL and NoSQL methods are both supported.Kudu combines the benefits of real-time processing with the capability for analytics. Learn more in the Apache Kudu Overview or visit the Kudu Repository on Github.

Because Kudu supports SQL, access is available via the standard JDBC interface. While you can certainly build new applications against Kudu, JDBC and SQL access also open Kudu to many existing off-the-shelf applications.
The Progress DataDirect JDBC driver for Impala leverages Kudu's tight integration with Impala. That integration allows you to insert, update, delete or query Kudu data along with several other operations.
With the flexibility to access Impala as well as Kudu, the Progress JDBC driver for Impala handles volume and velocity easily, and instantly works with popular BI and analytics tools.
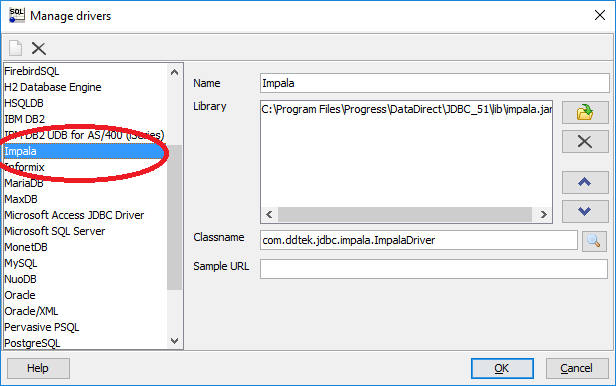
Ready to get started using SQL queries and JDBC against Apache Kudu? Check out this tutorial to walk you through the simple setup.

Saikrishna Teja Bobba
Saikrishna is a DataDirect Developer Evangelist at Progress. Prior to working at Progress, he worked as Software Engineer for 3 years after getting his undergraduate degree, and recently graduated from NC State University with Masters in Computer Science. His interests are in the areas of Data Connectivity, SaaS and Mobile App Development.
More from the author
Related Tags
Related Articles
Progress DataDirect Now Connects to Denodo
Progress DataDirect has added Denodo, a data virtualization software platform, to its catalog of connectors.
Progress DataDirect Achieves Google Cloud Ready—AlloyDB Designation
Progress DataDirect’s Drivers for Google AlloyDB offer a high-performing, secure and reliable connectivity solution for JDBC applications to access data in AlloyDB.
Top 5 Reasons to Use DataDirect with Salesforce
Customers pick Progress DataDirect for Salesforce connectivity because of its security, performance, high availability and more.
